Malignant Melanoma Cancer
Malignant Melanoma Cancer
We try to recommend the following in our practice. We try to recommend complete skin exams from head to toe every six months. We try to recommend all patients get into gowns for these exams. We try to recommend sunscreen SPF 30 or greater and avoidance of sun at peak hours between 10 to 2. Lastly, we educate our patients on what signs and symptoms to watch out for in terms of skin cancer. We try to recommend that if any growth on the body, changes, grows or bleeds, that you call our office immediately for evaluation of that growth.
What is Malignant Melanoma Skin Cancer?
The most serious form of skin cancer is Melanoma and it is the leading cause of death from skin disease. It begins in cells in the skin called melanocytes (cells that produce pigment and cause your skin to tan). Since most of these pigment cells are found in the skin, melanoma of the skin (cutaneous melanoma) is the most common form of melanoma.
Melanoma is more likely to spread to lymph nodes and other areas of the body compared to the other types of skin cancer (basal and squamous cell carcinoma). When melanoma spreads, it can spread to almost any other organ in the body but most commonly spreads to the liver, lungs, bones, and brain.
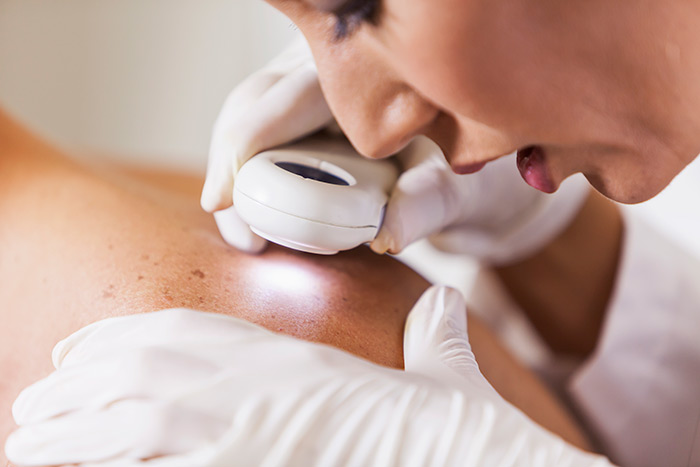
What Does Melanoma Look Like?
Often the first sign of melanoma is a change in the size, shape, color or feel of a mole. Most melanomas have a black or black-blue area. Melanoma may also appear as a new mole. It may be black, abnormal or look like an unusual mole.
Detection and Treatment
Melanoma most often develops in a pre-existing mole or looks like a new mole, which is why it is important for people to know what their moles look like and be able to detect changes to existing moles and spot new moles. Anyone who has more than 100 moles is at greater risk for melanoma. The first signs can appear in one or more atypical moles. It is imperative to get to know your skin very well and to recognize any changes in the moles on your body.
